

VLAN stacking is not needed for S-VLANs or on the M-VLAN. The reverse process happens for upstream traffic.
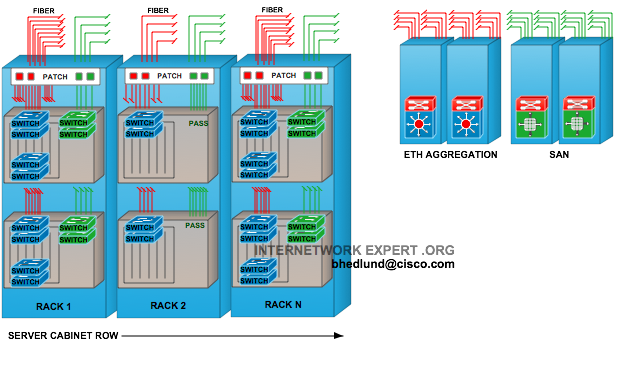
For downstream traffic, the Ethernet switch uses the outer tag to determine which port to forward the traffic to and will pop this tag before forwarding the traffic. In the last model, the traffic from the BSR to the switch includes two VLAN tags: an outer tag identifying the destination MSAN, and an inner tag identifying the subscriber on that MSAN. If there may be more than 4,095 subscribers per BSR port, then VLAN stacking (IEEE 802.1ad, also known as Q-in-Q) must be used. If there are (and always will be) less than 4,095 subscribers connected to a single BSR port, then the aggregation switch can transparently pass all VLANs. When using an aggregation switch with a C-VLAN topology, there are two situations to consider: 1. The 12-bit VLAN identifier supports up to 4,095 subscribers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
